Java数组03

AI-摘要
Rookie GPT
AI初始化中...
介绍自己 🙈
生成本文简介 👋
推荐相关文章 📖
前往主页 🏠
前往爱发电购买
Java数组03
Rookie_lArrays类
数组的工具类java.util.Arrays
由于数组对象本身并没有什么方法可以供我们调用,但API中提供了一个工具类Arrays供我们使用,从而可以对数据进行一些基本操作。
查看JDK帮助文档
Arrays类中的方法都是static修饰的静态方法,在使用的时候可以直接使用类名进行调用,而”不用“使用对象来调用(注意:是”不用”而不是“不能”)
具有以下常用功能:
- 给数组赋值:通过fill方法。
- 对数组排序:通过sort方法,按升序
- 比较数组:通过equals方法比较数组中元素值是否相等
- 查找数组元素:通过binarySearch方法能对排列好的数组进行二分查找法操作
代码实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18package com.xiheya.Array;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @Author {xiheya}
* @Date: 2022/03/12/ 16:19
* @Description
*/
public class ArrayDemo05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
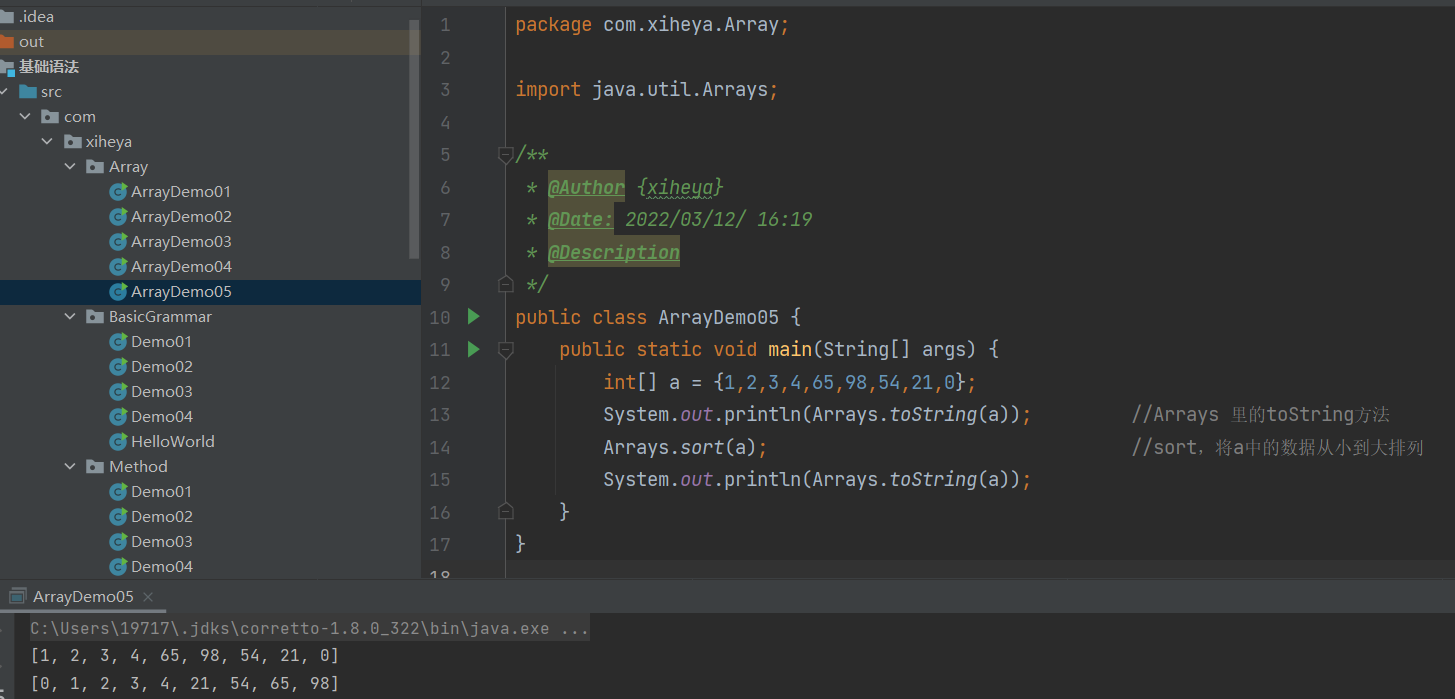
int[] a = {1,2,3,4,65,98,54,21,0};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); //Arrays 里的toString方法
Arrays.sort(a); //sort,将a中的数据从小到大排列
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));
}
}运行结果:
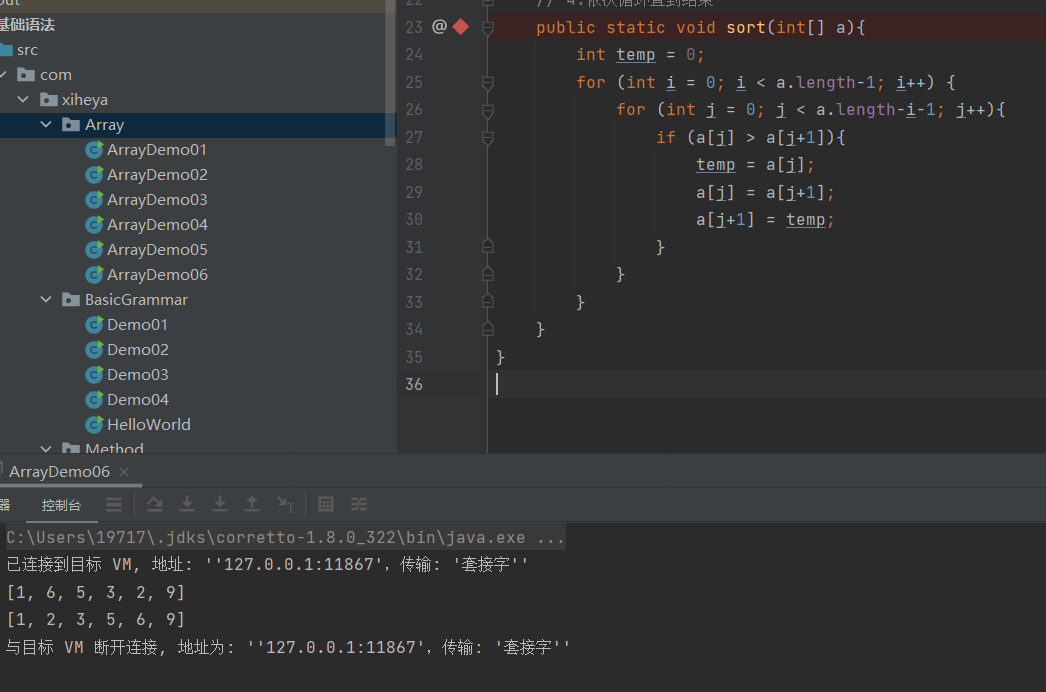
冒泡排序
- 冒泡排序是最出名的算法之一,总共有八大排序!
1 | package com.xiheya.Array; |
运行结果:
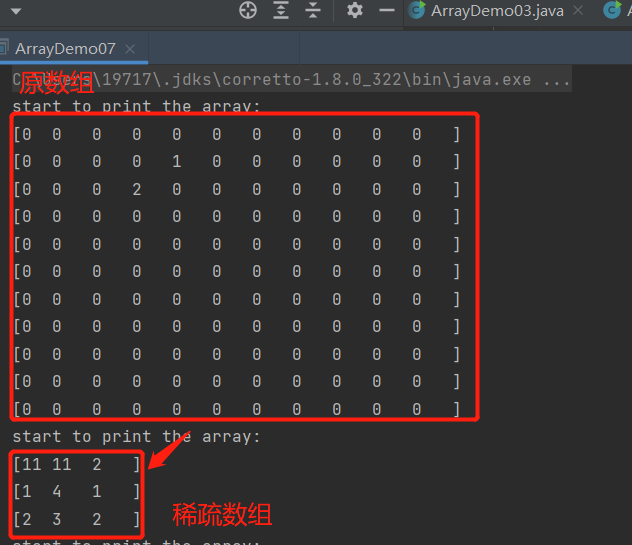
稀疏数组
- 需求:编写五子棋游戏中,有存盘退出和续上盘的功能。
- 介绍:当一个数组中大部分元素为0,或者为同一值的数组时,可以使用稀疏数组来保存该数组。
- 稀疏数组的处理方式是:
- 记录数组一共有几行几列,有多少个不同值
- 把具有不同值的元素和行列及值记录在一个小规模的数组中,从而缩小程序的规模
- 稀疏数组与原数组图示:
设计一个程序实现 稀疏数组与普通数组 的互换
代码:
1 | package com.xiheya.Array; |
运行结果:
评论
匿名评论隐私政策